Textile fibers
Textile fibers are defined as the basic building blocks of
textiles, which are materials made from interlacing fibers. Material filaments
are characterized as the essential structure blocks of materials, which are
materials produced using entwining strands. Material strands can be either
normal or engineered and can be turned into yarns and woven or sewed into
different materials. Material strands are utilized to create a large number of
items, including clothing, home decorations, modern items, and specialized
materials. A portion of the normal sorts of material filaments include:
- Regular filaments like cotton, fleece, silk, flax, and hemp
- Manufactured strands like polyester, nylon, acrylic, and spandex
- Cellulosic filaments like rayon, lyocell, and modular
- Glass filaments and carbon strands utilized in elite execution applications
The properties of material strands, like strength, flexibility, sturdiness, and protection from ecological elements, decide their reasonableness for different applications. The choice of filaments for a specific item relies upon the ideal properties and end-use prerequisites.
 |
| Flow Chart of Textile fibers |
Natural fibers
Natural fibers are fibers that are obtained from natural sources such as plants and animals. They are known for their delicateness, breathability, and biodegradability, which goes with them a famous decision for dress and materials. A few instances of regular strands include:
- Cotton - a delicate, spongy, and tough fiber that is ordinarily utilized in dress, sheet material, and home decorations
- Fleece - got from the wool of sheep and is known for its glow, protecting properties, and dampness wicking abilities
- Silk - a delicate, solid, and radiant fiber that is gotten from silkworms and is in many cases utilized in dress, sheet material, and home goods
- Flax - got from the stem of the flax plant and is known for its solidarity, toughness, and flexibility
- Hemp - a flexible fiber that is utilized in clothing, paper, and development materials
- Jute - a solid, coarse fiber that is ordinarily utilized in burlap and twine
These filaments are harmless to the ecosystem, inexhaustible, and biodegradable, which goes with them a famous decision for reasonable and eco-cognizant purchasers.
Synthetic fiber
Synthetic fiber are man-made filaments made from synthetic mixtures. They are intended to mirror the properties of regular filaments, yet offer improved solidness, strength, and protection from ecological factors like dampness, intensity, and UV light. A few instances of engineered filaments include:
- Polyester - utilized in dress, home goods, and modern applications
- Nylon - normally utilized in dress, ropes, and modern applications
- Acrylic - delicate and lightweight, utilized in attire and home goods
- Polypropylene - utilized in a large number of utilizations, including ropes, rugs, and geotextiles
- Spandex - known for its high versatility and utilized in apparel and materials
- Olefin - utilized in floor coverings, outside textures, and ropes
These filaments have upset the material business and are broadly utilized in various items because of their adaptability, reasonableness, and simplicity of support.
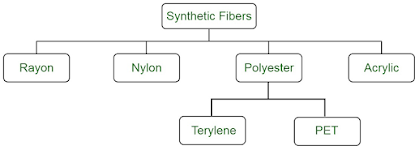 |
| Flow Chart of Synthetic Fibers |








0 Comments